Posterior superior alveolar artery
The posterior superior alveolar artery (posterior dental artery) is a branch of the maxillary artery. It emits branches that pass through foramina on the posterior aspect of the maxilla alongside the posterior superior alveolar nerves.[1]
| Posterior superior alveolar artery | |
|---|---|
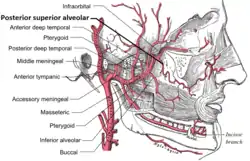 Plan of branches of maxillary artery | |
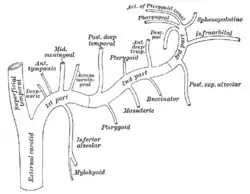 Plan of branches of maxillary artery. (Post. sup. alveolar in lower right.) | |
| Details | |
| Branches | branches to alveolar canals branches to gingiva |
| Supplies | molar and premolar teeth lining of the maxillary sinus gingiva |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria alveolaris superior posterior |
| TA98 | A12.2.05.075 |
| TA2 | 4444 |
| FMA | 49757 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Anatomy
Origin
The artery arises from maxillary artery as it is passing into the pterygopalatine fossa. It frequently arises conjunction with the infraorbital artery.
Branches
Descending upon the tuberosity of the maxilla, it divides into numerous branches, it descends on the posterior surface of the maxilla and gives branches that supply the molar and premolar teeth and the lining of the maxillary sinus, while others are continued forward on the alveolar process to supply the gingiva.
Additional images
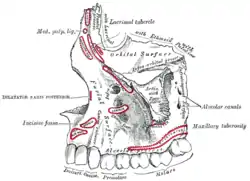 Left maxilla. Outer surface.
Left maxilla. Outer surface.
References
- Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). pp. 362–364. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 562 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 562 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)