Pontine cistern
The pontine cistern (also pontocerebellar cistern, or prepontine cistern[1]) is a subarachnoid cistern in the interval between ventral aspect of the pons, and the clivus. It contains the basilar artery.[2]: 478 The lateral aperture opens into the pontine cistern just posterior to the cranial nerve VIII.[2]: 483
| Pontine cistern | |
|---|---|
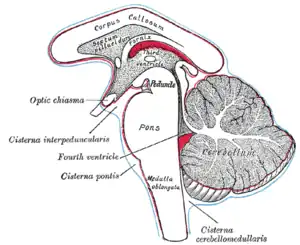 Diagram showing the positions of the three principal subarachnoid cisternæ. (Cisterna pontis labeled at left center.) | |
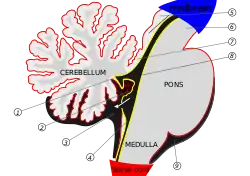 Scheme of roof of fourth ventricle. The arrow is in the foramen of Majendie. 1: Inferior medullary velum 2: Choroid plexus 3: Cerebellomedullary cistern of subarachnoid cavity 4: Central canal 5: Corpora quadrigemina 6: Cerebral peduncle 7: superior medullary velum 8: Ependymal lining of ventricle 9: Pontine cistern of subarachnoid cavity | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cisterna pontis, cisterna pontocerebellaris |
| NeuroNames | 556 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Anatomy
The pontine cistern is situated at the lateral aspects of the pons at its junction with the cerebellum. It may be subdivided into superior and inferior portions.[1]
It is continuous behind with the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord, and with the cisterna magna, and in front of the pons with the interpeduncular cistern.
References
- "Pontine cistern". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2023-06-08.
- Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 876 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 876 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)