Atogepant
Atogepant, sold under the brand name QULIPTA, is a medication used to prevent migraines. It is a gepant, an orally active calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRPR) antagonist.[1][2]
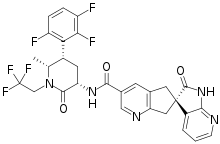 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Qulipta |
| Other names | AGN-241689, MK-8031 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H23F6N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 603.525 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
The neuropeptide CGRP controls cardiac excitability, microvascular permeability, vascular smooth muscle tone, and angiogenesis. It is broadly distributed in the central and peripheral nervous systems. By preferentially interacting with certain cell surface receptors, CGRP activates adenylate cyclase. It has recently been demonstrated that CGRP levels and the expression of CGRP receptors in the brain areas linked to migraine pathogenesis correlate with migraine attacks. In order to treat acute migraine headaches, CGRP receptor antagonists, also known as gepants, such as the therapeutic drugs atogepant, ubrogepant, and rimegepant, were created. In 2021, the US FDA authorized atogepant for use in treating adult patients who suffer from episodic migraines. [3]
Development timeline
In 2018, Allergan's oral CGRP receptor antagonist atogepant demonstrated robust efficacy and safety in episodic migraine prevention in a phase 2b/3 clinical trial. In 2020, AbbVie announced positive phase 3 data for atogepant in migraine prevention. In Mars 2021, U.S. FDA accepted AbbVie's new drug application for atogepant for the preventive treatment of migraine, then in September 2021, FDA approved Qulipta (atogepant) oral CGRP receptor antagonist for the preventive treatment of migraine, and approved it for adults with chronic migraine in 2023. Recently, AbbVie announced late-breaking results from phase 3 trial evaluating Qulipta for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine among patients with prior treatment failure. [4]
Medical Uses
Atogepant is indicated for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults.[1] A study found that atogepant reduced the number of migraine days over twelve weeks.[5]
Drug Interactions
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Co-administration of QULIPTA with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, results in a significant increase in exposure to atogepant. The recommended dosage of QULIPTA with concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin) is 10 mg once daily. However, when moderate or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors are used concurrently, there is no need to change the dosage of QULIPTA. [6]
CYP3A4 Inducers
Co-administration of QULIPTA with strong CYP3A4 inducers, results in a significant decrease in exposure of atogepant. Concomitant administration of QULIPTA with moderate inducers of CYP3A4 can also result in decreased exposure of atogepant. The recommended dosage of QULIPTA with concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s wort, efavirenz, etravirine) is 30 mg or 60 mg once daily. However, when weak CYP3A4 inducers are used concurrently, there is no need to change the dosage of QULIPTA. [6]
OATP Inhibitors
The recommended dosage of QULIPTA with concomitant use of OATP inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine) is 10 mg or 30 mg once daily. Co-administration of QULIPTA with single dose rifampin, an OATP inhibitor, resulted in a significant increase in exposure of atogepant in healthy subjects. [6]
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of QULIPTA is 10 mg, 30 mg, or 60 mg taken orally once daily with or without food. [6]
Dosage Modifications
Dosing modifications for concomitant use of specific drugs and for patients with renal impairment are provided in Table 1. [6]
| Dosage Modifications | Recommended Once Daily Dosage |
| Concomitant Drug | |
| Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors | 10 mg |
| Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers | 30 mg or 60 mg |
| OATP Inhibitors | 10 mg or 30 mg |
| Renal Impairment | |
| Severe Renal Impairment and End-Stage Renal Disease (CLcr <30 mL/min) | 10 mg |
Contraindications
None. [6]
Most Frequent Adverse Reactions
Nausea, constipation, fatigue/somnolence, decreased appetite. [6]
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
There are insufficient data on the potential developmental danger of QULIPTA usage during pregnancy. [6]
Lactation
There are no data on the presence of atogepant in human milk, the effects of atogepant on the breastfed infant, or the effects of atogepant on milk production. [6]
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. [6]
Geriatric Use
No clinically significant pharmacokinetic differences between elderly and younger people, according to population pharmacokinetic models. There were insufficient elderly patients included in QULIPTA clinical investigations to ascertain whether their responses differed from those of younger patients. The selection of a dose for an aged patient should generally be cautious, typically beginning at the low end of the dosing range reflecting the higher likelihood of reduced hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, as well as of concurrent disease or other pharmacological therapy. [6]
Renal Impairment
A small part in atogepant clearance is played by the renal route of elimination. The suggested dose of QULIPTA is 10 mg once daily for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and severe renal impairment (CLcr 15-29 mL/min and ˂15 mL/min, respectively). QULIPTA is best given right after dialysis for ESRD patients who get intermittent dialysis. For patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, there is no suggested dose adjustment. [6]
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment of QULIPTA is recommended for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Avoid use of QULIPTA in patients with severe hepatic impairment. [6]
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Atogepant is a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist. [6]
Pharmacodynamics
In cultured human coronary, cerebral, and middle meningeal arteries, atogepant reduced CGRP-induced vasodilatory responses; the inhibition was stronger in the cranial (i.e. cerebral and middle meningeal) arteries than the coronary arteries. In coronary arteries, atogepant did not exhibit any vasoconstrictive effects. In anaesthetized rats, pre-treatment with a combination of atogepant and onabotulinumtoxin A prevented activation/sensitization of high-threshold and wide-dynamic-range neurons in the spinal trigeminal nucleus. These nociceptive trigeminovascular neurons are hypothesized to play several functions in human pain perception, with central trigeminovascular pathway activation/sensitization being associated with headache perception. In a complete QT investigation, healthy adults receiving a single supratherapeutic dose of atogepant (300 mg) did not experience a clinically significant lengthening of the Fridericia-corrected QT interval. In a placebo-controlled study in healthy people, the once-daily administration of a supratherapeutic atogepant dosage (170 mg) for 28 days was not connected to any clinically relevant elevations in transaminase. Atogepant or the placebo had no effect on alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevations greater than three times the upper limit of normal (ULN), and mean blood ALT levels in both groups remained below the ULN throughout the research. [7]
Absorption
Atogepant is rapidly absorbed following oral administration of QULIPTA, with a median Tmax of 1–2 h. Atogepant exhibits dose-proportional pharmacokinetics after a once-daily dose up to 170 mg (about three times the highest recommended dosage), with no accumulation. The food effect was not noticeable when QULIPTA was given along with a high-fat meal (AUC and Cmax were decreased by about 18% and 22%, respectively, with no influence on the median time to maximum atogepant plasma concentration). In clinical efficacy investigations, QULIPTA was given without regard for food. [6]
Distribution
In the concentration range of 0.1 to 10 M, atogepant's plasma protein binding was not concentration-dependent; in human plasma, atogepant's unbound fraction was roughly 4.7%. After oral administration, atogepant's mean apparent volume of distribution (Vz/F) is approximately 292 L. [6]
Elimination
Atogepant is eliminated mainly through metabolism, primarily by CYP3A4. The two substances that were most frequently found circulating in human plasma were the parent substance (atogepant) and a glucuronide conjugate metabolite (M23). Atogepant has a half-life of elimination of about 11 hours. Atogepant has a mean apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of about 19 L/hr. After giving healthy male volunteers a single oral dose of 50 mg of 14C-atogepant, 42% and 5% of the dose were recovered as unmodified atogepant in the subjects' feces and urine, respectively. [6]
References
- "Qulipta- atogepant tablet". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 1 November 2021. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- Moreno-Ajona D, Pérez-Rodríguez A, Goadsby PJ (June 2020). "Gepants, calcitonin-gene-related peptide receptor antagonists: what could be their role in migraine treatment?". Current Opinion in Neurology. 33 (3): 309–315. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000806. PMID 32251023. S2CID 215408433.
- Wang, Qian; Han, Jianlin; Sorochinsky, Alexander; Landa, Aitor; Butler, Greg; Soloshonok, Vadim A. (14 August 2022). "The Latest FDA-Approved Pharmaceuticals Containing Fragments of Tailor-Made Amino Acids and Fluorine". Pharmaceuticals. 15 (8): 999. doi:10.3390/ph15080999. ISSN 1424-8247.
- Stewart, Judith. "Qulipta (atogepant) FDA Approval History". Drugs.com. Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- Ailani J, Lipton RB, Goadsby PJ, Guo H, Miceli R, Severt L, et al. (August 2021). "Atogepant for the Preventive Treatment of Migraine". The New England Journal of Medicine. 385 (8): 695–706. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035908. PMID 34407343. S2CID 237216018.
- "Highlights of prescribing information" (PDF). Food and Drug Administration. 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - Deeks, Emma D. (23 November 2021). "Atogepant: First Approval". Drugs. 82 (1): 65–70. doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01644-5. ISSN 0012-6667.