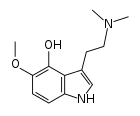
4-Hydroxy-5-methoxydimethyltryptamine
4-Hydroxy-5-methoxydimethyltryptamine, also known as 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT or psilomethoxin, is a hypothetical novel psychedelic drug. It is the 4-hydroxy counterpart of 5-MeO-DMT, or the 5-methoxy counterpart of psilocin.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 234.299 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 146 to 147 °C (295 to 297 °F) (from ethyl acetate[1]) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
It is structurally similar to other psychedelic tryptamines, but very little is known about its effects. The only report of it in the chemical literature was a paper published by Marc Julia's group at the Pasteur Institute in 1965.[1] This paper reports a 10 step synthesis of 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT from ortho-vanillin. Alexander Shulgin hypothesized that 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT could be biosynthesized by feeding Psilocybe cultures with 5-MeO-DMT, referencing a 1988 study by Jochen Gartz where transformation of DET into 4-HO-DET and 4-PO-DET was reported using such a method, with neither compounds having ever been found in nature.[2][3]
Legality
In the United States, 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT may be considered illegal under the Federal Analogue Act if sold or used for consumption due to structural relation to psilocin and 5-MeO-DMT, which are both listed as Schedule I controlled substances under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970.
An application to trademark the word "PSILOMETHOXIN" has been filed in the United States under code 045, though the registration has initially been refused (non-final office action issued on March 2, 2023).[4][5]
Religious use
4-HO-5-MeO-DMT is claimed to be used as a religious sacrament by the Church of Psilomethoxin. This entity was formed by the non-profit Church of the Sacred Synthesis and is based in Texas.[6][7] The organization has also attempted to trademark the word ‘PSILOMETHOXIN’ for its use.[4][5]
On April 12th, 2023 a preprint study was published that analyzed the claimed sacrament sold by the church. The sample was not found to contain any 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT, nor any 5-MeO-DMT, and appeared to have been typical Psilocybin mushroom material containing psilocybin and psilocin, with a trace amount of baeocystin.[8] In response to this study, The Church of Psilomethoxin issued a statement.[9] This church’s statements have been criticized by some.[10]
References
- Julia M, Manoury P, Voillaume MC (1965). "No 209 - Recherches en série indolique. XIV (*) - Sur des méthoxy-5 hydroxy-4, méthoxy-5 hydroxy-6 et méthoxy-7 hydroxy-6 tryptamines". Bulletin de la Société Chimique de France (in French): 1417–1423.
- "4-Hydroxy-5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, Psilocybe mushrooms, Psilocin". Ask Dr. Shulgin Online. Retrieved 2023-04-29.
- Gartz J (1989). "Biotransformation of tryptamine derivatives in mycelial cultures of Psilocybe". Journal of Basic Microbiology. 29 (6): 347–352. doi:10.1002/jobm.3620290608. PMID 2614674. S2CID 43308695.
- "PSILOMETHOXIN Trademark of Church of the Sacred Synthesis - Serial Number 97342001". Alter.
- U.S. Trademark 97,342,001
- "Church of Psilomethoxin". Church of the Sacred Synthesis.
- "Church of the Sacred Synthesis". opencorporates.com.
- Williamson S, Sherwood A (12 April 2023). "Fungi Fiction: Analytical Investigation into the Church Of Psilomethoxin's Alleged Novel Compound Using UPLC-HRMS". ChemRxiv. American Chemical Society (ACS). doi:10.26434/chemrxiv-2023-bxxtl.
- "Psychedelic capitalism". Church of the Sacred Synthesis. Archived from the original on 13 April 2023.
- Nickles, David (28 April 2023). "Church of Psilomethoxin, Part 1: Sacramental Skepticism. Is the Church in Denial?". Psymposia. Retrieved 2023-06-18.