Brilaroxazine
Brilaroxazine (developmental code names RP-5063 and RP-5000), also known as oxaripiprazole,[1][2] is an investigational atypical antipsychotic which is under development by Reviva Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.[4][5][6][7][8] Reviva Pharmaceuticals also intends to investigate brilaroxazine for the treatment of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, psychosis/agitation associated with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease psychosis, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADD/ADHD), and autism.[9][10] As of July 2023, it is in phase III clinical trials for schizophrenia.[9][10]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | RP-5063; RP-5000; Oxaripiprazole[1][2] |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >99% |
| Metabolism | Liver (mostly via CYP3A4 (64%) and 2D6 (17%)) [3] |
| Elimination half-life | 42-48 hours [4] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25Cl2N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 450.36 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Brilaroxazine is described as a so-called "dopamine-serotonin system stabilizer" due to its unique actions on the dopamine and serotonin neurotransmitter systems compared to other antipsychotics.[4][11] Specifically, it acts as a potent partial agonist of the D2, D3, and D4, 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors, and as an antagonist of the 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors.[4][8][11] Brilaroxazine exhibits high affinity for the D2S, D2L, D3, D4.4, 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT7 and H1 receptors, and moderate affinity for the D1, D5, 5-HT2C, 5-HT3, 5-HT6 and α4β2 nicotinic receptors, the serotonin transporter, and the α1B-adrenergic receptor.[4][8][11] It lacks significant affinity for the 5-HT1B, α2-adrenergic, and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, as well as for the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters.[11]
| Site | Ki (nM) | Action | |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 100 | ND | |
| D2L | 0.45 | Partial agonist | |
| D2S | 0.28 | Partial agonist | |
| D3 | 3.7 | Partial agonist | |
| D4 | 6.0 | Partial agonist | |
| D5 | 200 | ND | |
| 5-HT1A | 1.5 | Partial agonist | |
| 5-HT2A | 2.5 | Partial agonist | |
| 5-HT2B | 0.19 | Antagonist | |
| 5-HT2C | 39 | Antagonist | |
| 5-HT3 | 78 | ND | |
| 5-HT6 | 51 | Antagonist | |
| 5-HT7 | 2.7 | Antagonist | |
| H1 | ND | ND | |
| α4β2 nicotinic | 36.3 | ND | |
| SERT | 107 | ND | |
| Values are Ki (nM). The smaller the value, the more strongly the drug binds to the site. | |||
Chemistry
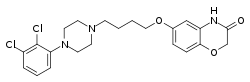
Brilaroxazine is identical to aripiprazole in chemical structure except for the replacement of one of the carbon atoms in aripiprazole's quinolinone ring system with an oxygen atom, resulting instead in a benzoxazinone ring system. The drug is also closely related structurally to brexpiprazole and cariprazine.
Recent Developments
In June 2023, Reviva Pharmaceuticals announced successful enrollment over 80% of the participants in its schizophrenia phase III clinical trial. This pivotal study, which includes clinical sites across the United States, Europe, and Asia, aims to assess the efficacy and longer term safety of brilaroxzaine in schizophrenia. A letter from the CEO released in January 2023 noted no major adverse drug effects were observed as of that date and that enrollment was progressing well. The anticipated study completion date is late 2023. If successful, commercial availability is anticipated in 2026.
References
- Modica MN, Lacivita E, Intagliata S, Salerno L, Romeo G, Pittalà V, Leopoldo M (October 2018). "Structure-Activity Relationships and Therapeutic Potentials of 5-HT7 Receptor Ligands: An Update". J Med Chem. 61 (19): 8475–8503. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01898. PMID 29767995.
- Jordan, Ann Westcot (14 September 2018). Antidepressants: History, Science, and Issues. ISBN 9781440839276.
- Cantillon M, Ings R, Prakash A, Bhat L (2018). "A Population Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of RP5063 Phase 2 Study Data in Patients with Schizophrenia or Schizoaffective Disorder". European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 43: 573–585. doi:10.1007/s13318-018-0472-z. PMID 29619682.
- Cantillon M, Prakash A, Alexander A, Ings R, Sweitzer D, Bhat L (2017). "Dopamine serotonin stabilizer RP5063: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter trial of safety and efficacy in exacerbation of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder". Schizophrenia Research. 189: 126–133. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2017.01.043. PMID 28215471.
- Rajagopal L, Kwon S, Huang M, Michael E, Bhat L, Cantillon M, Meltzer HY (2017). "RP5063, an atypical antipsychotic drug with a unique pharmacologic profile, improves declarative memory and psychosis in mouse models of schizophrenia". Behavioural Brain Research. 332: 180–199. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2017.02.036. PMID 28373127.
- Medicines in Development for Mental Health (PDF) (Report). Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. 2014. p. 20. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
- Köster LS, Carbon M, Correll CU (December 2014). "Emerging drugs for schizophrenia: an update". Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs. 19 (4): 511–31. doi:10.1517/14728214.2014.958148. PMID 25234340. S2CID 42729570.
- "Drug Development in Schizophrenia: Summary and Table". Pharmaceutical Medicine. 28 (5): 265–271. 2014. doi:10.1007/s40290-014-0070-6. ISSN 1178-2595. S2CID 8513976.
- "About Us". Reviva Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
- "Product Pipeline". Reviva Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
- Marc Cantillon, M.D., Mike Li, MS, Sarath Kanekal, Ph.D., DABT, RAC, Robert M.J. Ings, Ph.D., Grace Tung, RAC, Laxminarayan Bhat (2013). "Refresh: A Phase 2 RP5063 Efficacy and Safety in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder" (PDF). American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Product Pipeline - Reviva Pharmaceuticals
- Brilaroxazine (RP 5063) - AdisInsight
- RP5063
- Brilaroxazine
- Oxaripiprazole
- Press Releases - Reviva Pharmaceuticals